GUM PROBLEMS (Periodontal disease)

In fact, this is the leading cause of tooth loss amongst adults because it is virtually pain-free, many patients do not know they have the disease.
WHAT CAUSES GUM DISEASE?
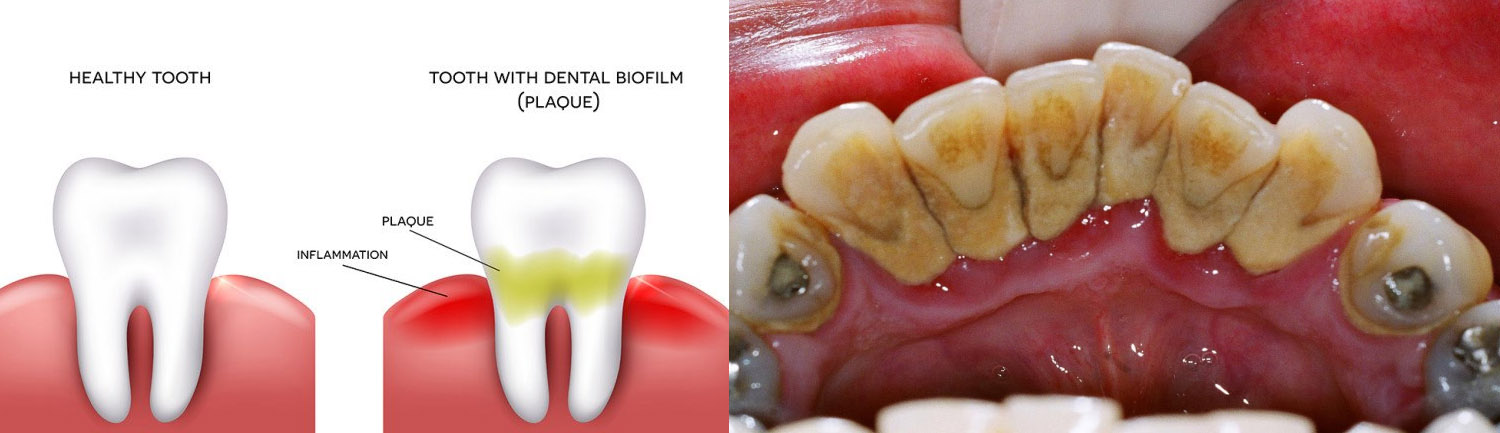
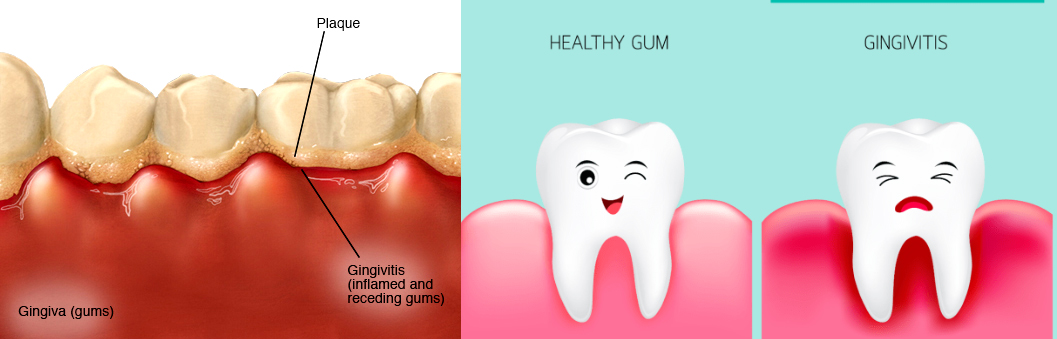
It is caused by a buildup of plaque that will harm not only the gums surrounding a tooth, but also the connective tissues and bone structure beneath the gums.
If the plaque is not removed (by flossing, brushing, and regular dental checkups), it will continue to build up and create toxins that can damage the gums. When the underlying connective tissue and bone are extensively damaged, tooth loss is the result.
Periodontal disease forms just below the gum line and create small pockets that separate the gums from the teeth. Periodontal disease has two stages: gingivitis and periodontitis.

SYMPTOMS OF GUM DISEASE:
Gum disease is most effectively and conveniently treated in its earliest stages. An early diagnosis of gum disease can mean the difference between non-surgical treatment and invasive gum surgery.
There are a number of symptoms of gum disease which, if present, should be immediately addressed by a dentist.
Common symptoms of gum disease include:
- Bleeding gums
- Gums that have pulled away from the teeth
- Bad breath
- Sensitive, swollen, or red gums
- Loose teeth
- Increased space between teeth
- The formation of pus between teeth & gums
- Mouth sores
Some factors increase the risk of developing gum disease. They are:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Crooked teeth that are hard to keep clean
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
- Medications, including steroids, certain types of anti-epilepsy drugs, cancer therapy drugs, some calcium channel blockers and oral contraceptives
- Bridges that no longer fit properly
TREATING GUM DISEASE:
Treatments for gum disease can vary depending on the severity of each individual case. Typical treatments include:
- Non-surgical treatments such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning)
- Periodontal surgery and laser gum surgery
- Dental implants
PREVENTING GUM DISEASE:
Regular dental checkups and periodontal examinations are important for maintaining your health and the health of your smile.
You don’t have to lose teeth to periodontal disease, and by practicing good oral hygiene at home, you can significantly reduce your chances of ever getting gum disease. Remember to brush regularly, clean between your teeth, eat a balanced diet, and schedule regular dental visits to help keep your smile healthy.